Glass Solution
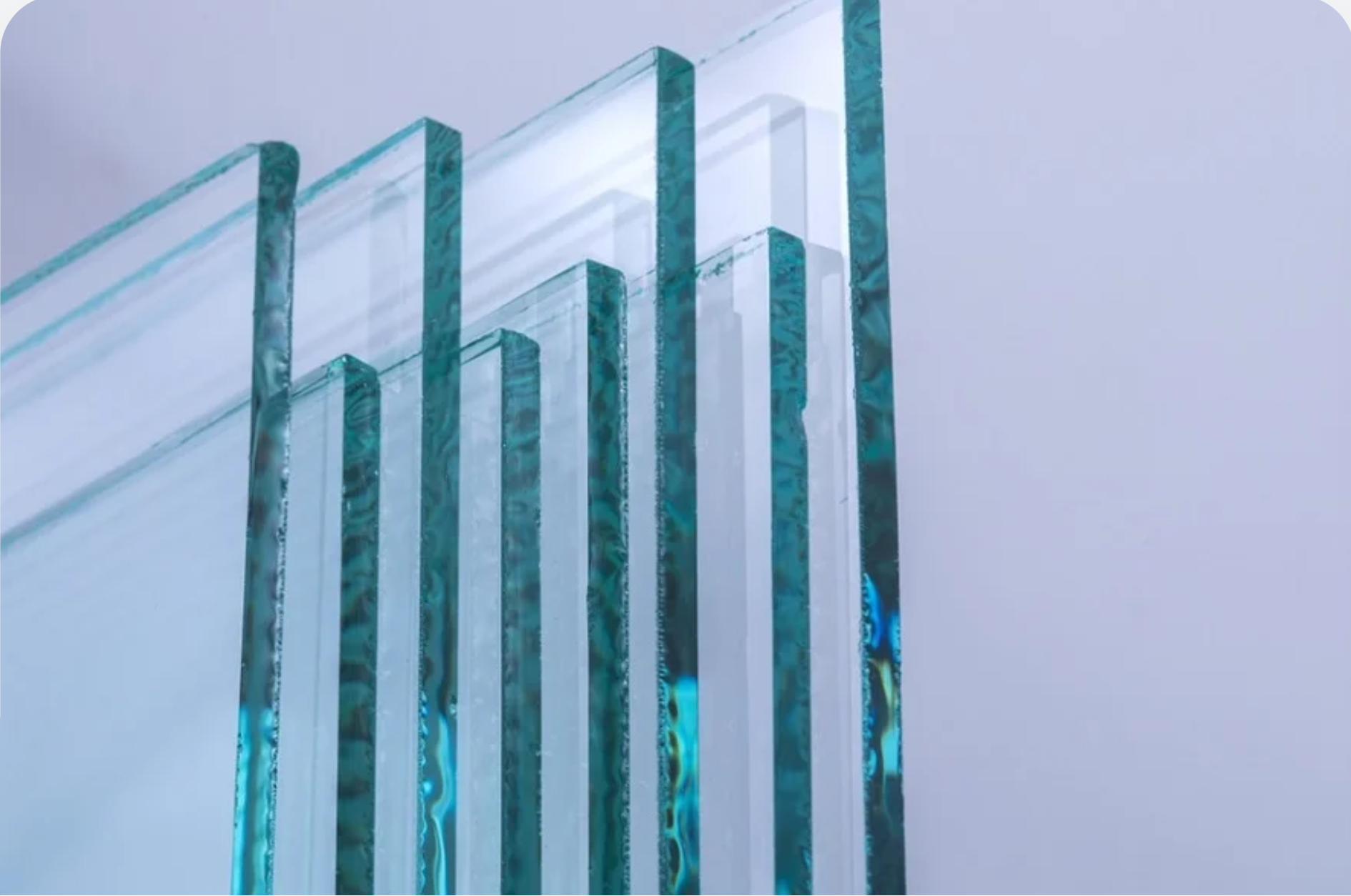

Float Glass
The most common type of glass made by floating molten glass on molten tin, resulting in a flat, uniform thickness.
Used For:
- ● Windows and doors
● Mirrors (when coated with reflective backing)
● Table tops and shelves
Tempered Glass (Toughened Glass)
Glass that has been heat-treated to increase its strength and safety. When it breaks, it shatters into small, blunt pieces.
Used For:
- ● Car windows
● Shower enclosures
● Storefronts and facades
● Glass doors and partitions
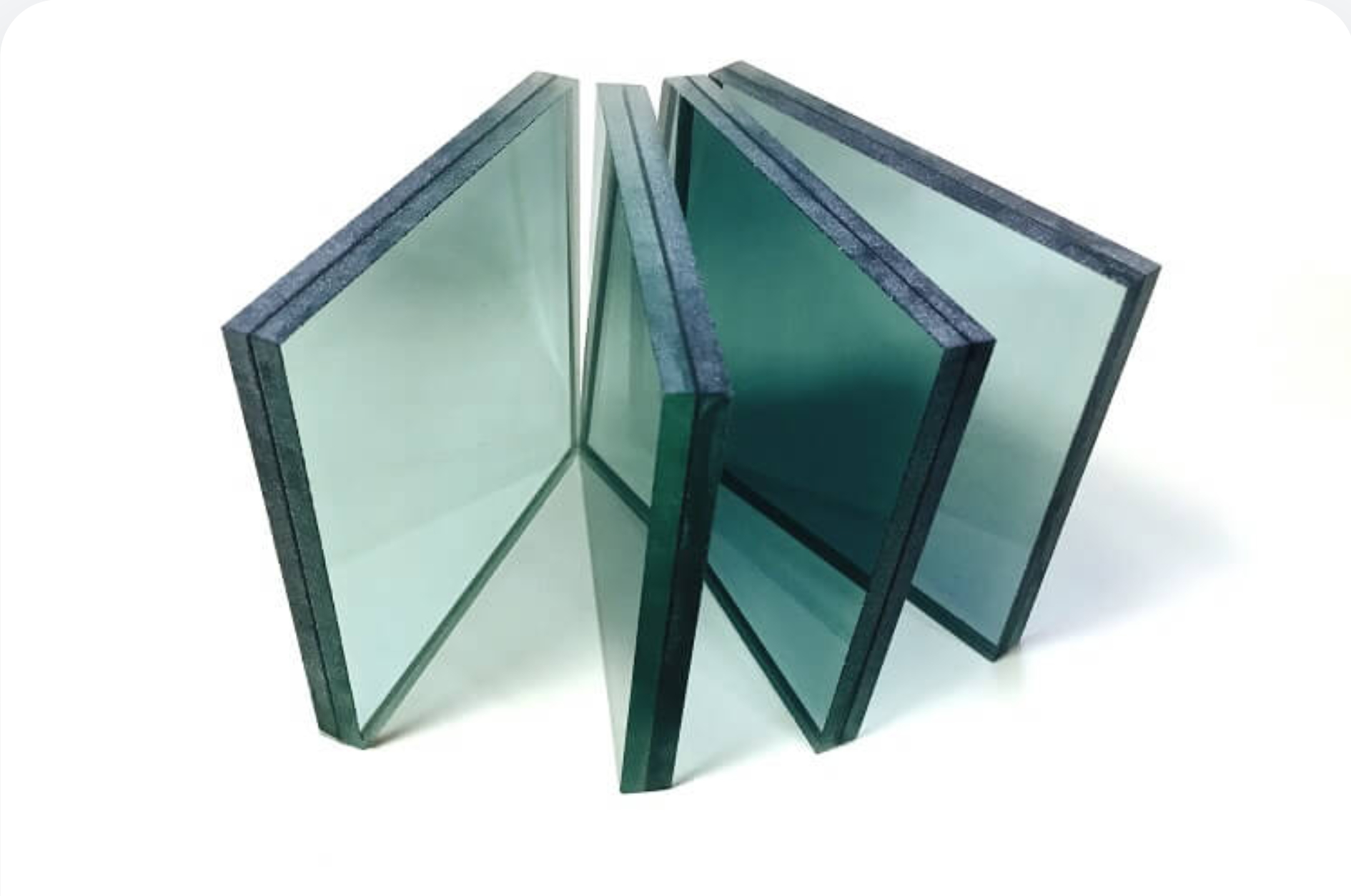

Laminated Glass
Two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer (usually PVB or EVA) that holds pieces together if broken.
Used For:
- ● Windshields (vehicles)
● Skylights
● Balconies and railings
● Security glass and soundproof windows

Low-E (Low Emissivity)
What it is: Glass coated with a thin metallic oxide layer to control heat transfer — keeps heat in during winter and reflects heat during summer.
Used For:
- ● Energy-efficient building windows
● Modern architecture and skyscrapers

Acoustic Glass
Laminated glass with a special acoustic interlayer designed to reduce noise transmission.
Used For:
- ● Airports and hotels near highways
● Urban residential buildings
● Office partitions
● Modern architecture and skyscrapers
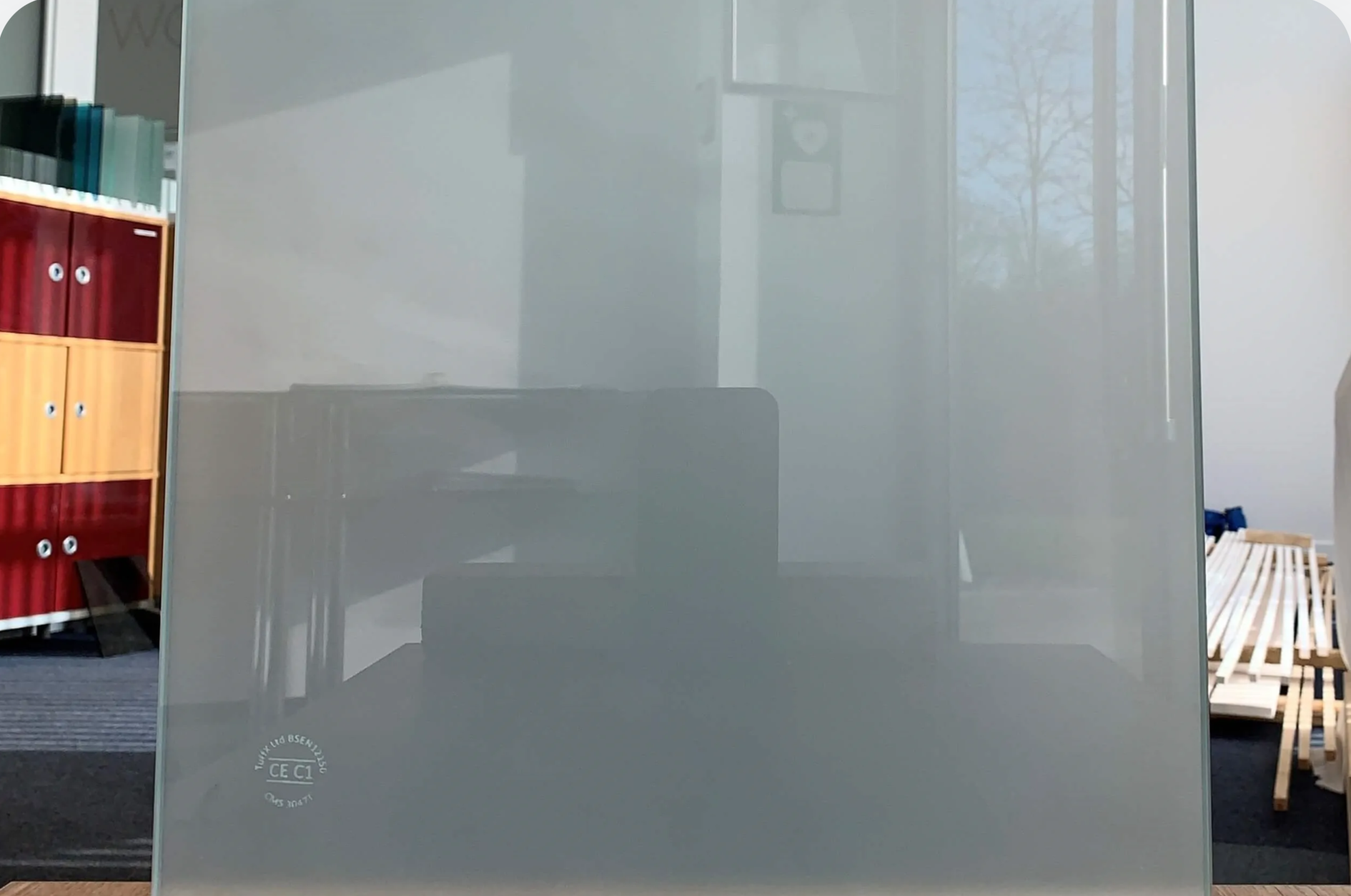

Frosted / Etched Glass
Glass that has been sandblasted or acid-etched to give a translucent, matte finish.
Used For:
- ● Bathroom windows
● Office partitions
● Decorative panels
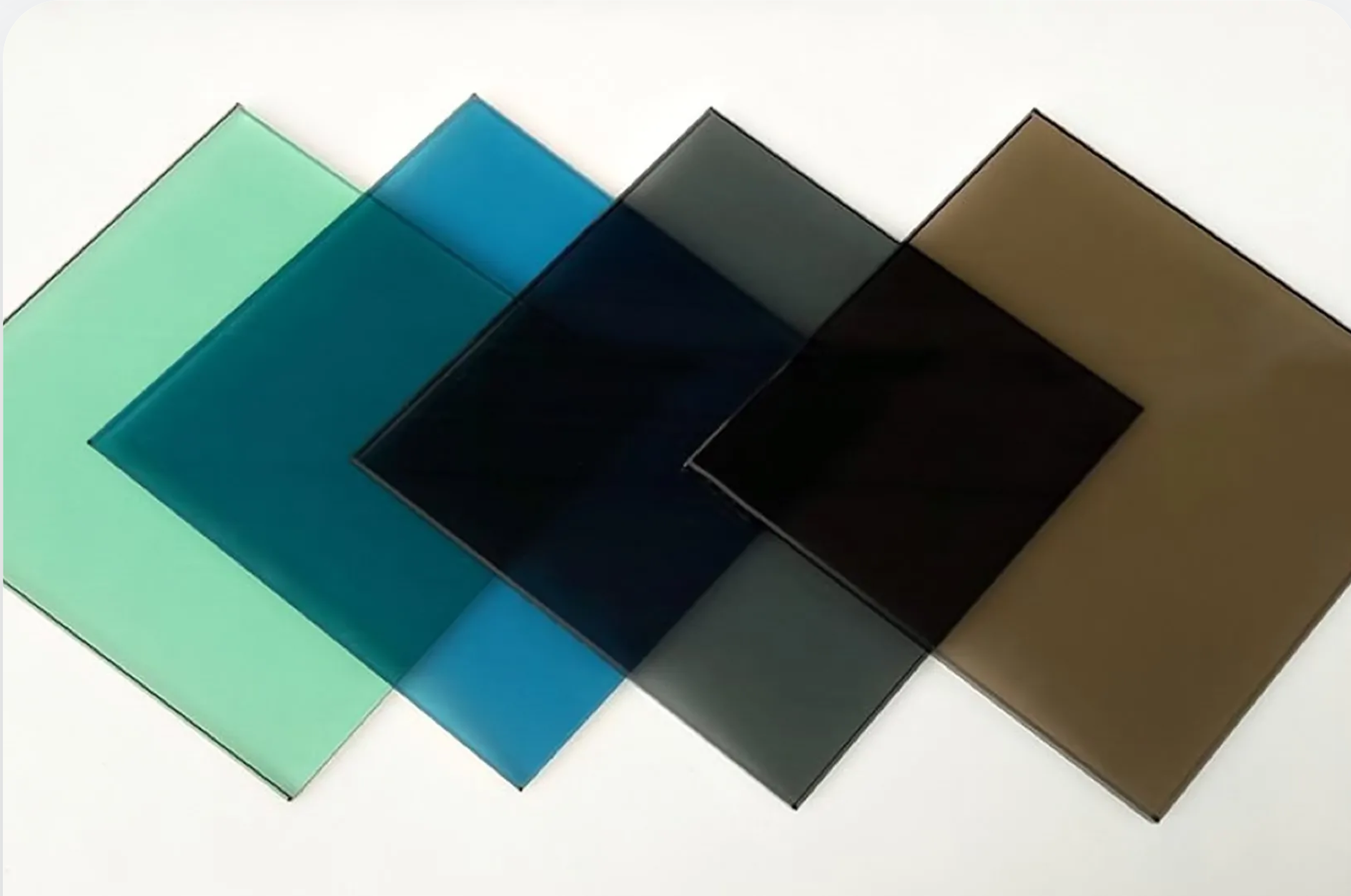

Tinted Glass
Glass with color additives (gray, bronze, blue, or green) that reduce glare and solar heat.
Used For:
- ● Commercial buildings
● Cars and skylights
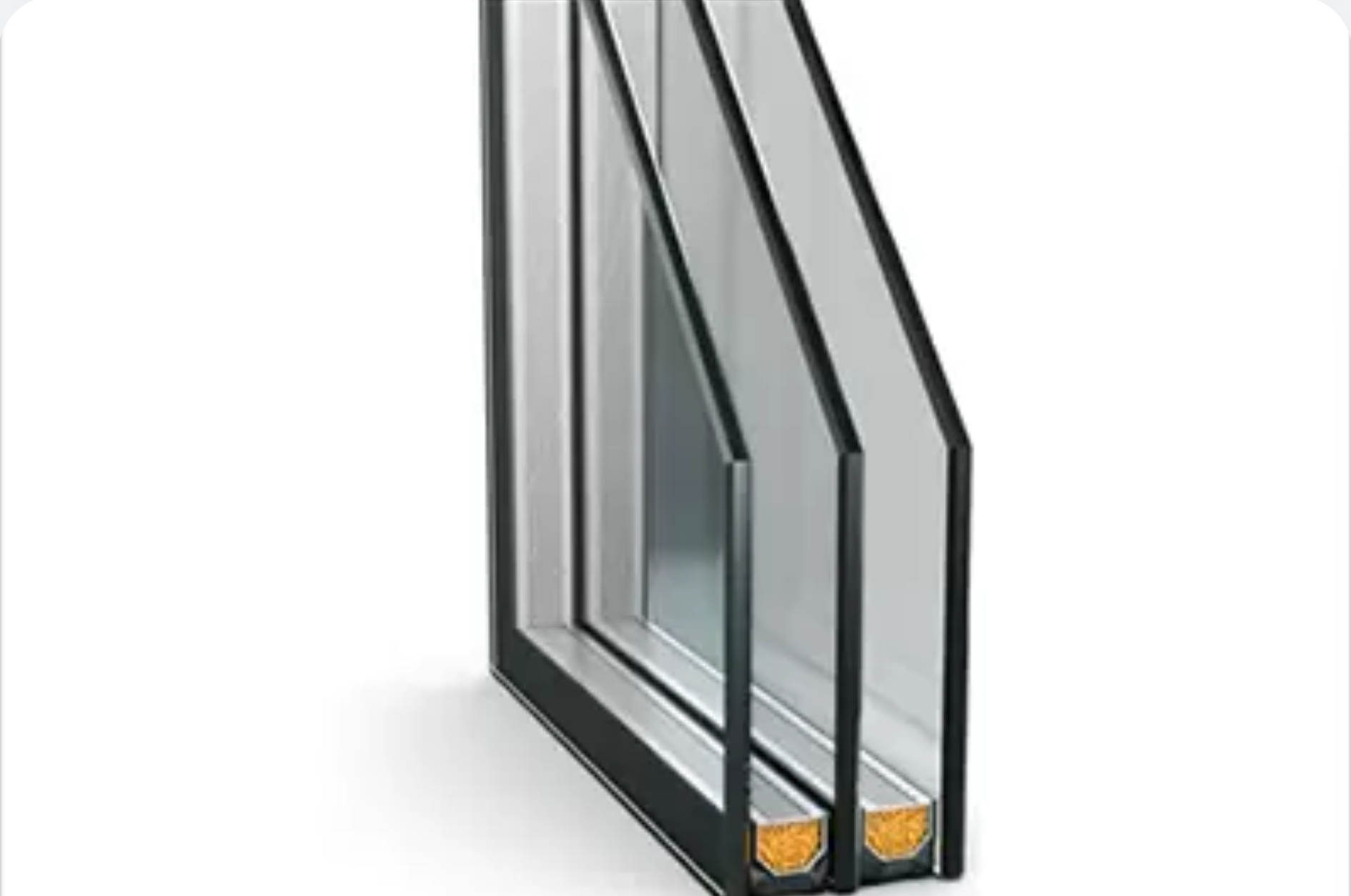

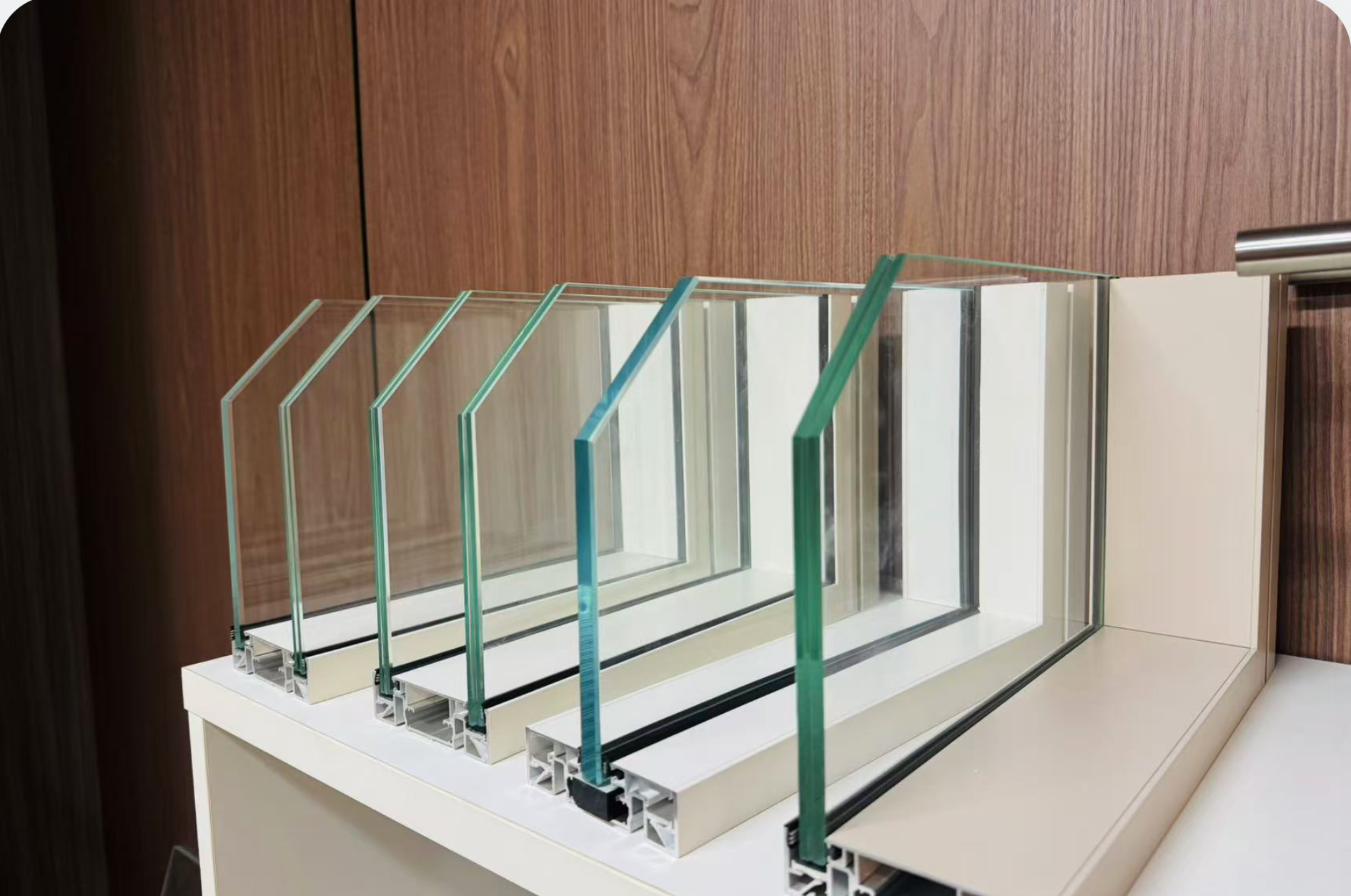
Insulated Glass Units (Double / Triple Glazed)
Two or more glass panes separated by an air or gas-filled space to reduce heat transfer.
Used For:
- ● Residential and Commercial windows
● Climate-controlled buildings
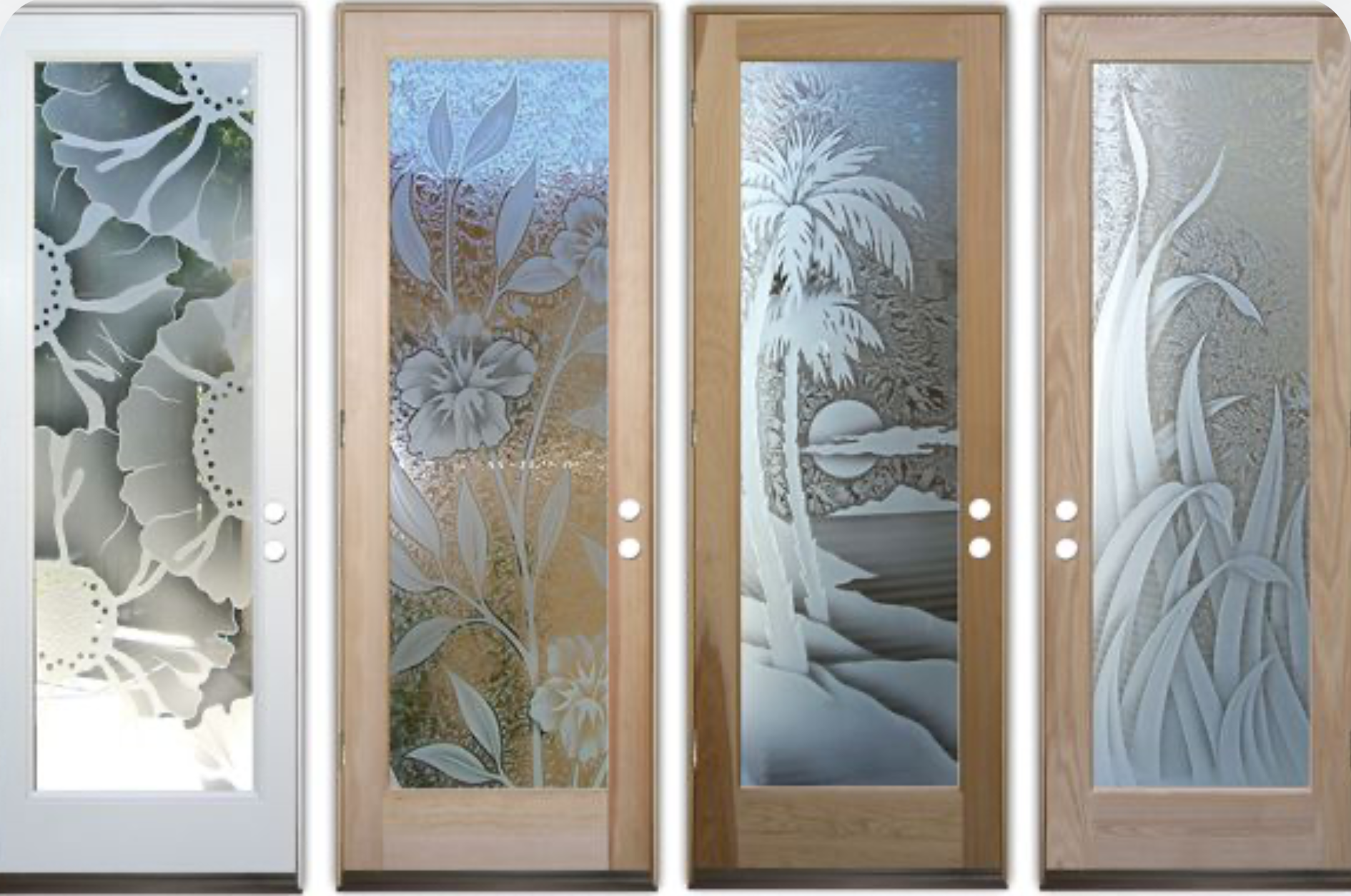

Decorative / Patterned Glass
Glass embossed or printed with patterns for design or privacy.
Used For:
- ● Interior Decoration
● Doors, partitions, and bathroom panels
